Setting up an SSH Key for GitHub
For detailed instructions, visit this documentation on github.
In this process, you will create two keys:
-
A private key that is stored on your local machine
-
A public key that is stored on Github
This public/private key pair is used to securely transfer data from your local machine to the server hosted by Github. In other words, the keys are used by git to
-
download changes from the remote repository to your local repository (e.g. using
pullorclone) -
upload changes from the local repository to the remote repository (e.g.
push)
1. Generate a new SSH key
On your local machine, open a terminal and execute the ssh-keygen command.
$ ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "your_email@example.com"
Generating public/private ed25519 key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/alinen/.ssh/id_ed25519):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /home/alinen/.ssh/id_ed25519
Your public key has been saved in /home/alinen/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:cUr7fXShYj7lz1Rly2TVXQ/tIwg3FPkv/co7BSJBfEA your_email@example.com
The key's randomart image is:
+--[ED25519 256]--+
| +E+o ..|
| .o+. .|
| o +o+ =+|
| . =...o*o=|
| S + +=++|
| .o.+o +o|
| .o..oo.|
| .o= .|
| +* |
+----[SHA256]-----+Notes
-
The
-Coption indicates a comment. Replace this with your own information. -
Typing ENTER for the file location will choose the default
-
Typing ENTER for the password will disable a password for this key
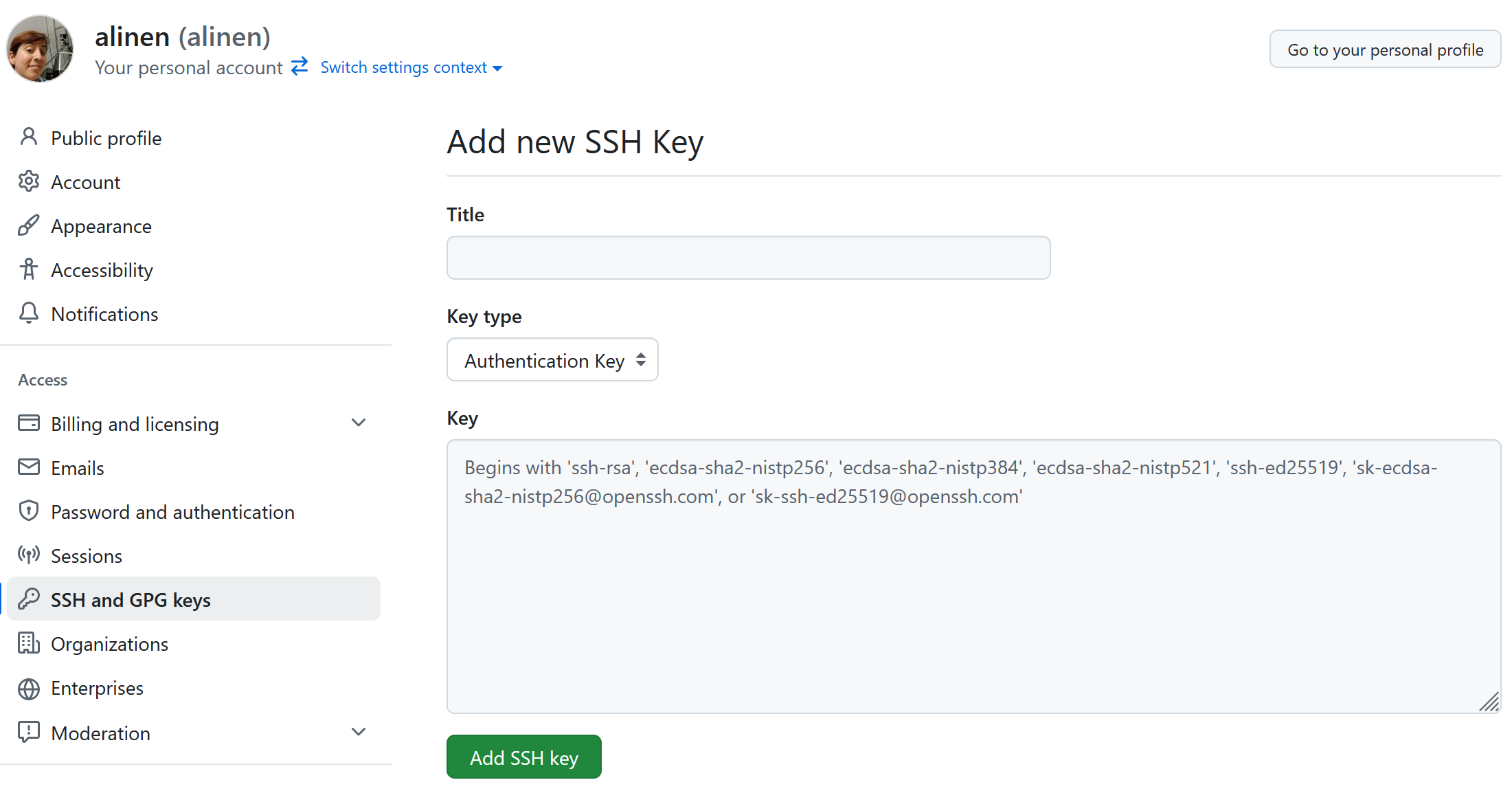
2. Add your SSH key to GitHub
Copy the key to your clipboard. Check the contents of ~/.ssh. You should
see a private key (name: id_ed25519) and a public key (name: id_ed25529.pub).
$ ls ~/.ssh/
id_ed25519 id_ed25519.pub known_hosts known_hosts.old
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIBNxuU/ZMS5DfKqdtq6Fd1XPfgMLy/f4KCG0j0+RQ4T0 your_email@example.comWe need to give the public key to Github. Copy the entire contents of id_ed25519.pub and
paste it to your GitHub Settings.
-
In the upper-right corner of any page on GitHub, click your profile picture, then click Settings.
-
In the "Access" section of the sidebar, click SSH and GPG keys.
-
Click New SSH key or Add SSH key.
-
In the "Title" field, add a descriptive label for the new key. For example, if you’re using a personal laptop, you might call this key "Personal laptop".
-
Select key type authentication.
-
In the "Key" field, paste your public key.
Click Add SSH key.
3. Test your key
Run the following command.
$ ssh -T git@github.com
Hi alinen! You've successfully authenticated, but GitHub does not provide shell access.You should see a success message.
Troubleshooting Tips
How to check for an existing SSH key
SSH keys are typically stored in .ssh in your home directory.
ls -al ~/.sshWhat if no agent is running?
If you get an error saying that the SSH agent is not running, use the following command to start it. This command can be placed in your ~/.bashrc file so it runs automatically every time you log into bash.
Start the agent and add your key:
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_ed25519