Study Guide - Midterm 01
Midterms are closed book. You can bring one written cheat sheet. 80 minutes in class.
Topics:
-
C programming: arrays, functions, pointers, strings
-
Data type formats: signed and unsigned integers, ASCII characters
-
Bitwise operators, bit fields
-
Binary arithmetic
-
Boolean algebra, truth tables
-
Gates, R-S Latches, Adders, Multiplexors, Demultiplexors
-
von Neuman architecture and its typical components: CPU, ALU, PC, IR, Registers, bus, RAM, Input and Outputs
-
Instruction pipeline: Fetch, decode, execute, store
-
Hack ALU design
-
Hack assembly and machine code
-
Hack CPU design: inputs and outputs
Binary, hex, and bitwise operations
-
Convert the following binary numbers to hexadecimal.
-
0110 1010
-
1110 0011
-
0110 1110
-
-
Convert the following hexadecimal numbers to binary.
-
0xF5
-
0x03
-
0x2D
-
-
Convert the following numbers to decimal.
-
0b 0101 (as a 4-bit signed and unsigned integer)
-
0b 1000 (as a 4-bit signed and unsigned integer)
-
0x 0101
-
0x B4
-
-
Compute the results of the following decimal expressions using 4-bit unsigned integers. Express your final answer in hexadecimal. Show your work.
Expression |
Result |
3 << 8 |
|
2 & 7 |
|
-
Compute the results of the following decimal expressions using 4-bit signed integers. Express your final answer in hexadecimal. Show your answer.
Expression |
Result |
-6 >> 3 |
|
2 ^ 7 |
|
-
Consider the following program
1 #include <stdio.h>
2
3 int main() {
4 unsigned char a = 0x7E;
5 unsigned char leftMask = 0xC0;
6 unsigned char rightMask = 0x03;
7 unsigned char left = (leftMask & a) ;
8 unsigned char right = (rightMask & a) ;
9 unsigned char leftShift = left >> 4;
10 unsigned char rightShift = right << 4;
11 unsigned flipped = leftShift | rightShift;
12 }-
What is the value of
ain binary? -
What is the value of
flipped? Show your work to give a rationale for your answer. -
Suppose we have a 4-bit bit field that stores whether an animal can fly, swim, or walk, defined with the following masks
#define NONE 0x0
#define FLY 0x1
#define SWIM 0x2
#define WALK 0x4-
Suppose an animal’s bitfield contains the value 0x3. What capabilities does it have?
-
What value would the bitfield have for an otter, which can swim and walk?
-
What value would the bitfield have for a duck, which can fly, swim and walk?
-
What value would the bitfield have for a cow, which can only walk?
Programming
-
Draw the function stack for the following program.
void mystery(int a, int b, int* c)
{
*c = a & b;
}
int main()
{
int a = 7;
int b = 8;
int c = 0;
mystery(a, b, &c);
return 0;
}-
Draw the function stack for the following program.
char mystery(char a)
{
unsigned char x = a & 0x01;
unsigned char y = x << 6;
unsigned char z = a >> 1;
unsigned char result = y | z;
return result;
}
int main()
{
char word[32];
strncpy(word, "woohoo", 32); // w = 0x77, o = 0x6F, h = 0x68
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
word[i] = mystery(word[i]);
}
return 0;
}-
Draw the function stack for the following program
void foo(int A[4])
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
A[i] = ~A[i];
}
}
void main()
{
unsigned char input[4];
foo(input);
}Von Neuman Architecture
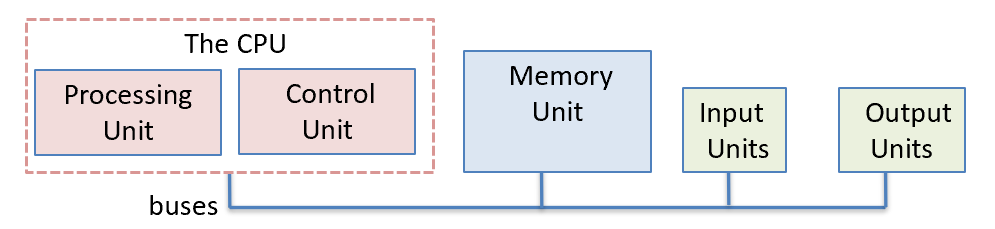
-
What are four primary components of the von Neuman architecture?
-
What components does a central processing unit typically have in a von Neuman architecture?
-
List and describe the four steps of instruction execution.
-
What is instruction pipelining?
-
What is the purpose of the PC register?
-
What is the purpose of the IR register?
-
What is the bus in a von Neuman architecture?
Circuits and Hardware Design
-
Give an example of how abstractions are used in hardware design to build up complex functionality from simple components.
-
In regards to circuits, what is the different between sequential and combinatorial logic?
-
What is a half-adder? A full-adder?
-
What is a ripple carry adder?
-
What is a ripple carry adder?
-
What is the purpose of the gate in a gated D-latch?
-
Can an R-S Latch ever produce inconsistent output?
-
Give the truth tables for And, Or, Not, Nand, and Xor.
-
Draw the truth table that corresponds to this circuit.
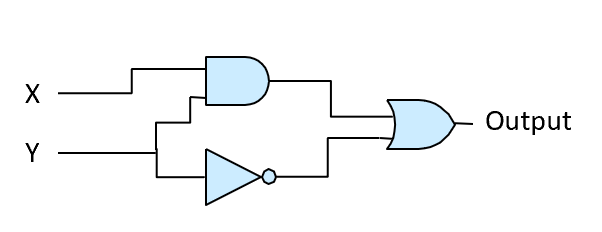
-
Design a gate that implements this truth table
A |
B |
Out |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
-
Draw the circuit and truth table corresponding to the Boolean expression
~A | B -
Draw the circuit that corresponds to the Boolean expression
(s & a)|(~s & b) -
Draw the truth table for a 1-bit adder circuit. From this table, give a Boolean expression for each of the outputs.
-
Design a circuit for the following truth table
A |
B |
C |
Out |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
-
Suppose you have a 4-bit adder, xor, not, and, or chips. Show how you can build a 4-bit chip that can either add and subtract, e.g.
-
Inputs: 4-bit A, 4-bit B, 1-bit flag where 0 means add and 1 means subtract
-
Outputs: 4-bit result
-
-
Suppose you have eight 16-bit Gated D-latch chips (aka data flip-flops (DFFs)) combined in a single memory unit. How many bits are needed to address this memory? Draw a diagram that shows how multiplexors and demultiplexors can be used to build an addressable read/write memory for 8 registers.
-
Consider the following Gated D-Latch built with nand gates. Suppose a = 1 and b = 0. How does the state of the gate change if the user sets Data to 0 and WE to 0?
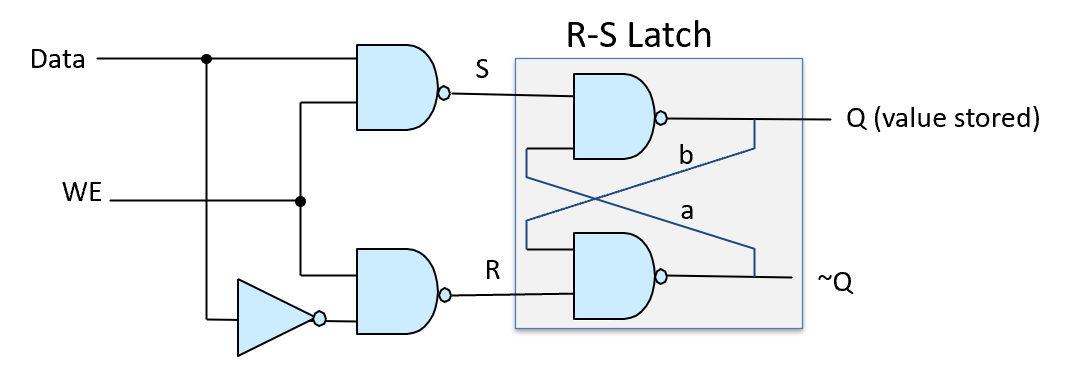
-
In a gated D-latch, what is the purpose of the gate?
-
How can multiple 1-bit DFFs be combined to create an 8-bit register? Draw a diagram.
-
What is the purpose of the clock in a von Neuman architecture? (Name two reasons)
-
Consider the following diagram from the data sheet of a 4-bit adder. What should the values of each pin be if we use this chip to calculate 5 + 4?
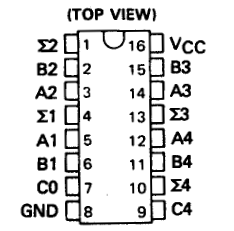
Hack ALU
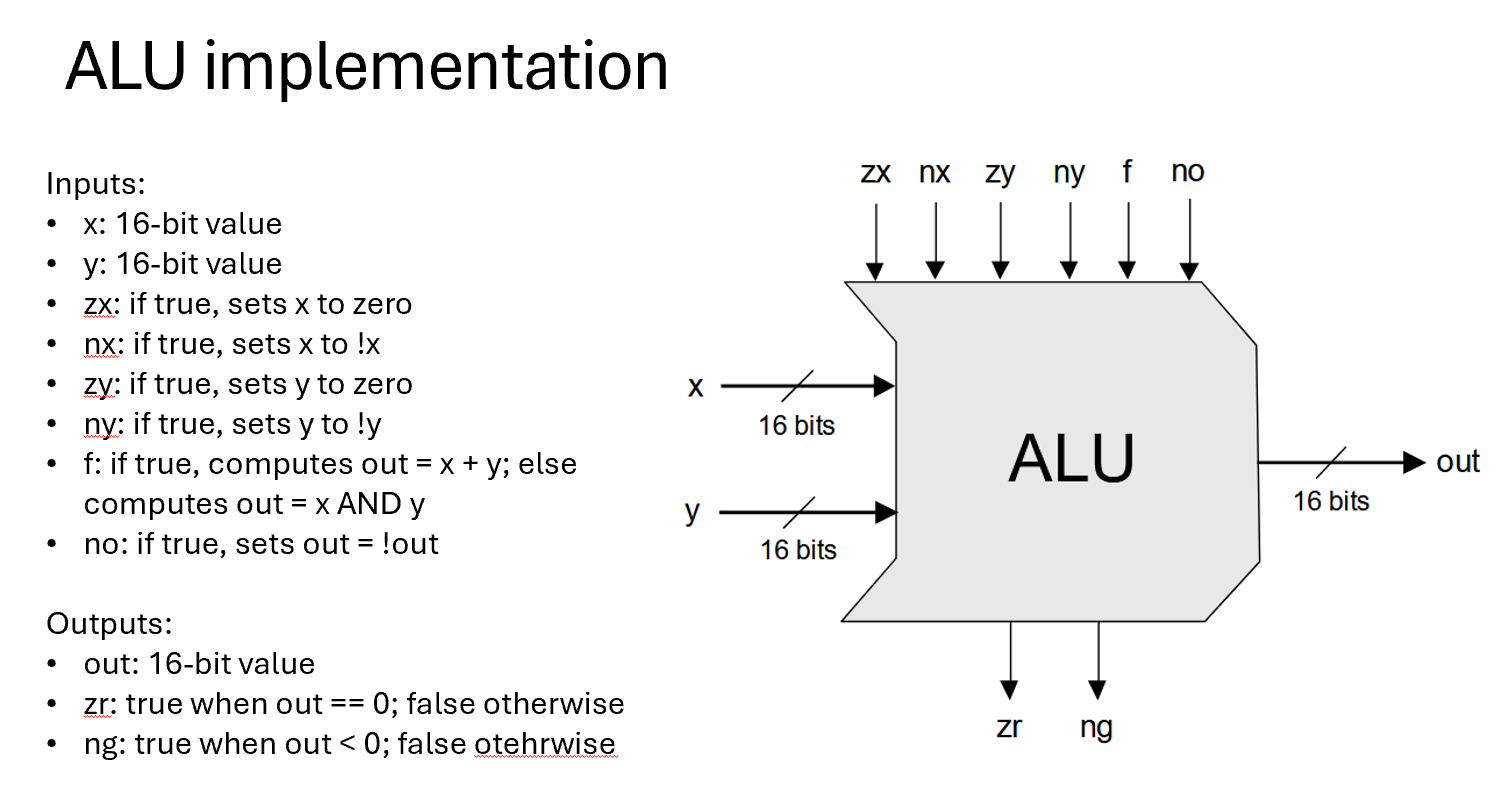
-
Suppose we input X=7, Y=7, and (zx, nx, zy, ny, f, no) = (0,0,0,0,0,0). What is the value of out, ng, and zr?
-
Suppose we input X=7, Y=7, and (zx, nx, zy, ny, f, no) = (0,0,0,0,1,0). What is the value of out, ng, and zr?
-
Suppose we input X=7, Y=7, and (zx, nx, zy, ny, f, no) = (1,1,1,1,1,1). What is the value of out, ng, and zr?
Hack Counter
Recall the counter circuit that takes four inputs: an input value (In), a reset flag, an increment flag (Inc), and a load flag. The following timeline shows how the values of reset, inc, and load change over time. Suppose In = 5 and is constant throughout. If out = 27 to start, how does it value change with the inputs?
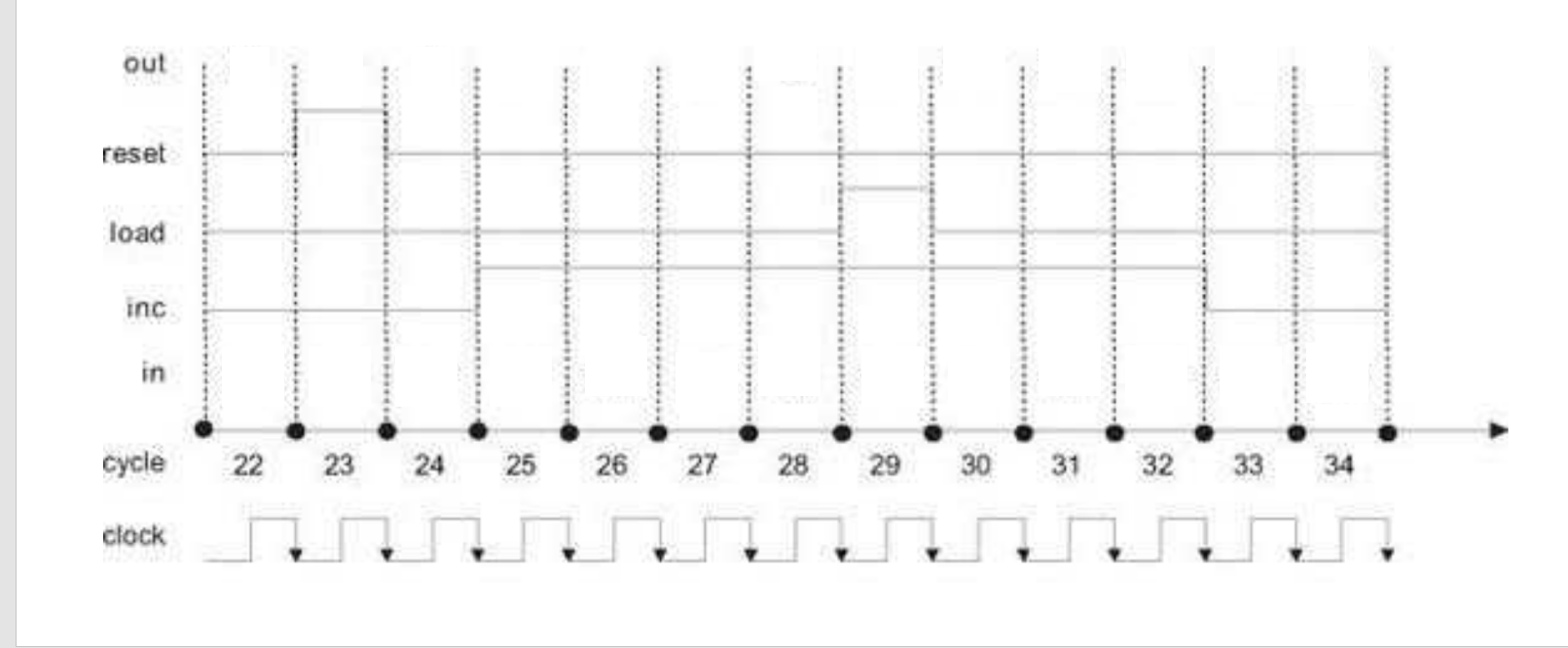
Hack Assembly and machine code
The Hack assembly language has the following syntax.
-
A-instruction
-
@aaa where aaa is a non-negative number
-
-
C-instruction
-
dest = comp; jump, where
jumpcan be one of {null, JGT, JEQ, JGE, JLT, JNE, JLE, JMP} anddest = comphave one of three forms-
reg = {0|1|-1} where reg = {A|D|M}
-
reg1 = reg2 where reg1 = {A|D|M} and reg2 = [-]{A|D|M}
-
reg = reg1 op reg2 where reg1 = {A|D|M}, reg2 = {A|D|M|1}, and op = {+|-|&||}
-
-
The Hack assembly language maps to machine code as follows:
-
A-instruction
-
0vvv vvvv vvvv vvvvwhere v is 1-bit (0 or 1)
-
-
C-instruction
-
111a cccc ccdd djjj
-
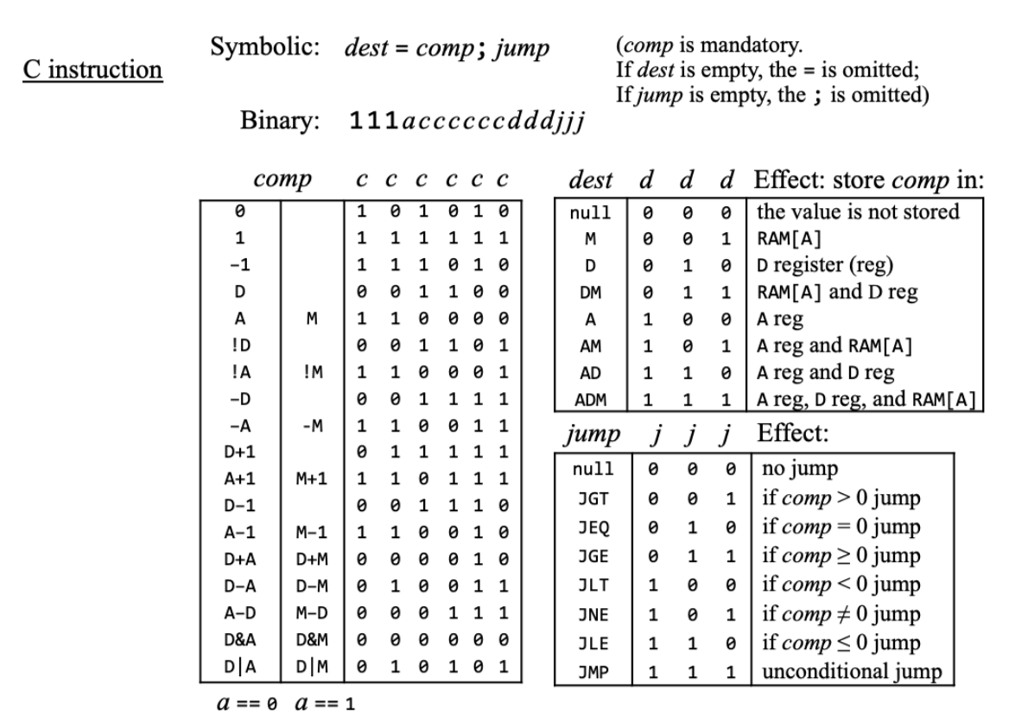
-
Is the expression
M=45a valid assembly instruction? -
Is the expression
A=1a valid assembly instruction? -
Is the expression
A=D+1a valid assembly instruction? -
Write Hack assembly for the following expressions
-
A ← 43
-
D ← 0
-
R[100] ← 0
-
R[100] ← 17
-
RAM[3] ← RAM[4] + 1
-
-
Write a Hack program that implements the following algorithm
i = 4
sum = 3
while (i-- >= 0)
{
sum = sum + 3
}
-
Fill in the contents of memory and registers for the following Hack assembly program. Assume the first instruction is stored at address 0 in ROM.
@5 D=A @8 D=M+D @9 D;JNE
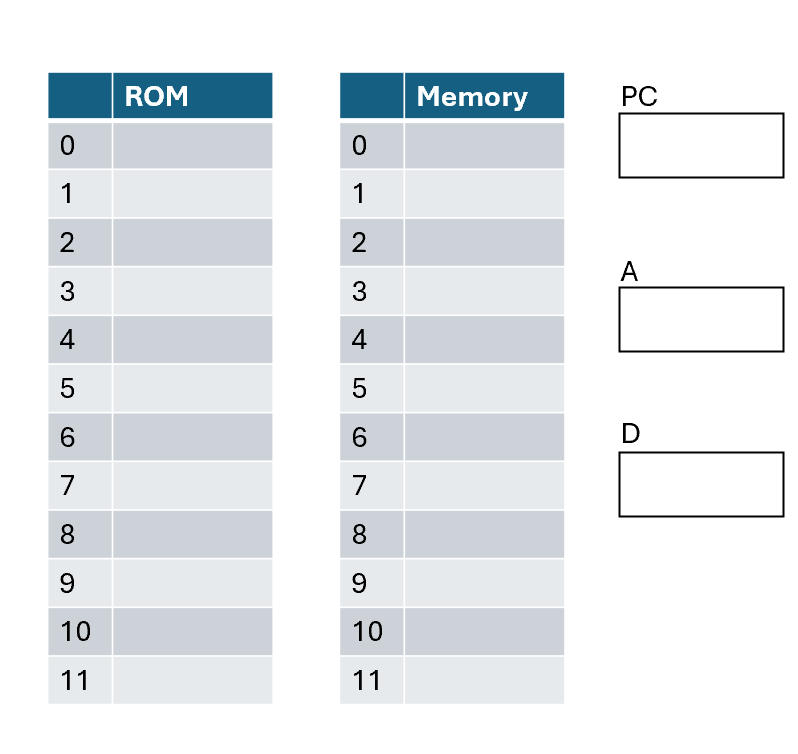
-
Convert the following Hack Assembly commands to machine code
-
D=M+D
-
@9
-
D;JNE
-
-
Recall the CPU design from your book The Elements of Computing Systems.
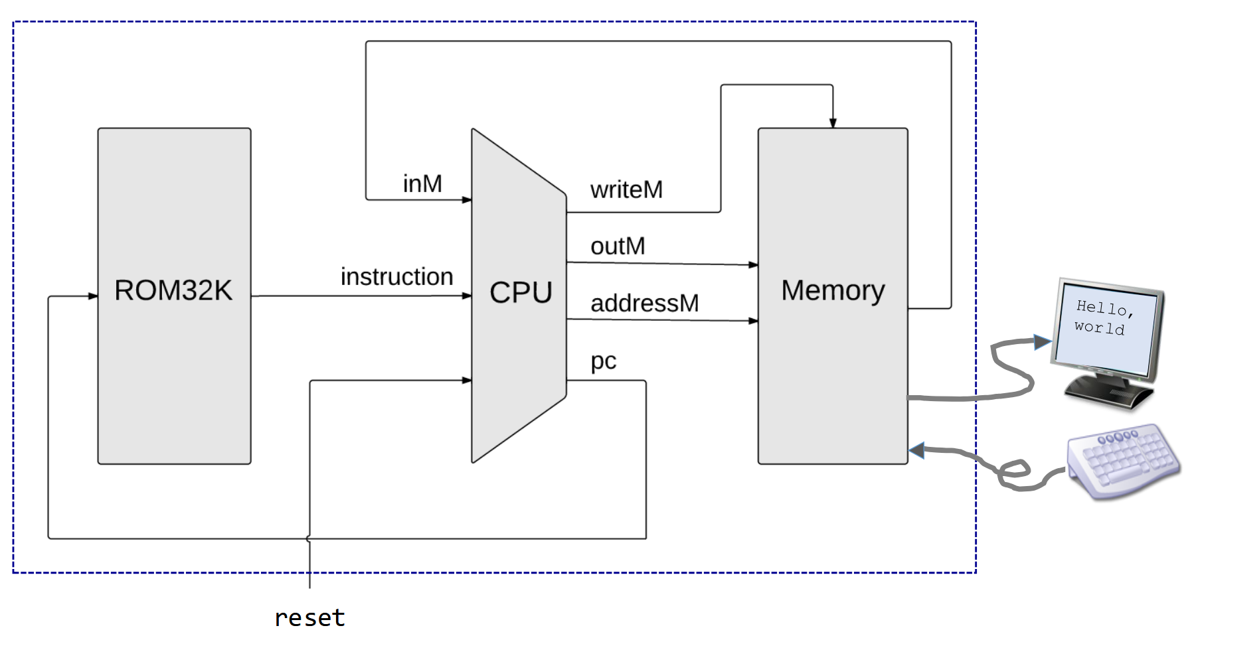
-
Suppose the CPU has the following state and inputs: inM = 0x50, reset = 0, D = 0x8, A = 0xA, PC = 0x3, addressM=0x100, outM=0x35, writeM=0
-
How will the contents of PC, D, A change as a result of running the instruction "D=M"?
-
How will the contents of PC, D, and A change as a result of running the instruction "@37"?
-
How will the contents of PC, D, and A change as a result of running the instruction "D;JGT"?
-
How will the contents of PC, D, and A change as a result of running the instruction "D=D+1"?
-
How will the contents of writeM, outM, and addressM change as a result of running the instruction "M=M-1"?
-
How will the contents of writeM, outM, and addressM change as a result of running the instruction "D=M-1"?
-